Features, Applications, and Advantages of Thermoplastic Compression Molds
- Suase /
- SUASE NEWS
Definition of Thermoplastic Compression Molds
Thermoplastic compression molds are specialized molds used for forming thermoplastic materials. Thermoplastic materials soften when heated and harden when cooled, allowing them to be repeatedly reheated and reshaped. Thermoplastic compression molds are widely used in industries such as automotive, electronics, electrical appliances, and construction due to their high production efficiency and stable product performance.
Material Selection for Thermoplastic Compression Molds
- P20 Steel: Offers strong toughness and wear resistance, suitable for mass production.
- H13 Steel: Provides excellent heat crack resistance, ideal for processing complex mold structures.
- S136 Stainless Steel: Known for its strong corrosion resistance, suitable for high-gloss finish products.
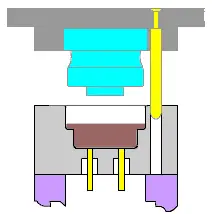
Manufacturing Process of Thermoplastic Compression Molds
The manufacturing process of thermoplastic compression molds involves several precise steps, including:
- Mold Design: Conduct 3D modeling based on product requirements to ensure a reasonable structure that meets compression molding process demands.
- CNC Machining: Utilize CNC machines for precise cutting to meet tolerance and geometric requirements.
- Heat Treatment Process: Perform quenching, tempering, and other heat treatment steps to enhance mold hardness and wear resistance.
- Polishing and Surface Treatment: Conduct fine polishing and chrome plating to improve product surface finish and demolding performance.
Application Fields of Thermoplastic Compression Molds
Thermoplastic compression molds play an important role in various industries:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Widely used in producing automotive interior parts, bumpers, dashboards, door panels, and other components.
- Electronics and Appliances: Suitable for producing various appliance housings, switch panels, and electronic device components.
- Home and Building Materials: Used in plastic furniture, bathroom accessories, and window and door frames.
- Packaging Containers: Including plastic bottle caps, food containers, and cosmetic packaging.
Advantages of Thermoplastic Compression Molds
- High Production Efficiency: Thermoplastic materials have short heating and cooling cycles, significantly improving production speed.
- Stable Product Quality: Thermoplastic compression molds ensure high dimensional accuracy, smooth surface finish, and reduced defect rates.
- Strong Design Flexibility: Thermoplastic compression molds can produce complex curved surfaces and precision-structured parts.
- Excellent Material Recyclability: Thermoplastic plastics are recyclable and meet environmental requirements.
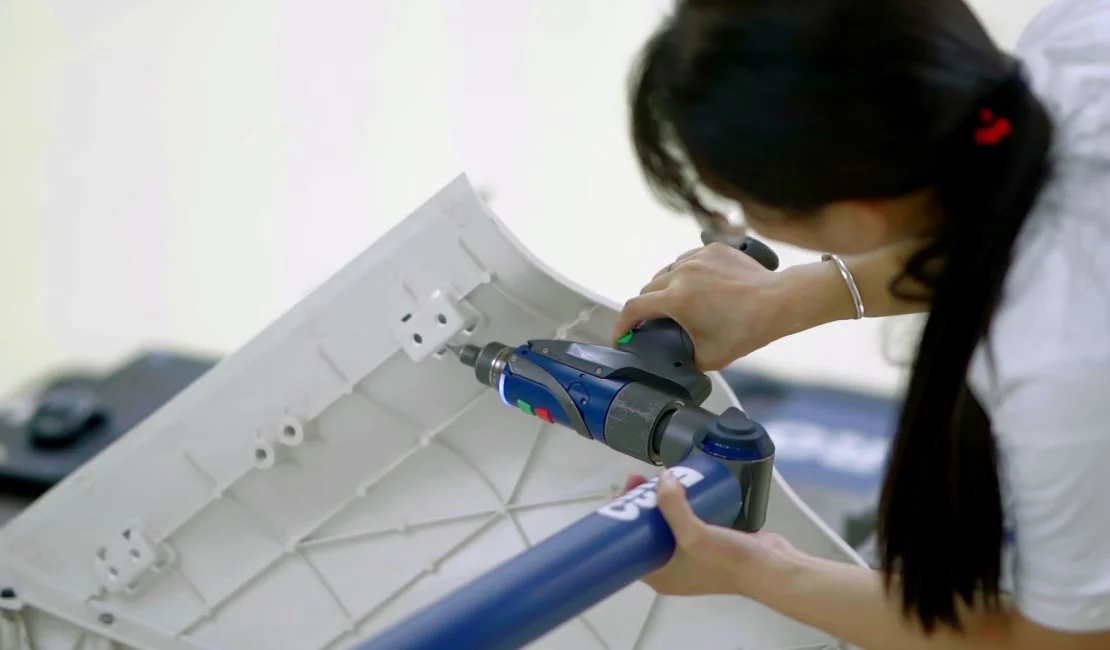

Maintenance and Care of Thermoplastic Compression Molds
- Regular Cleaning: Residual material should be cleaned from the mold after each production run to prevent clogging and carbon buildup.
- Lubrication Maintenance: Apply lubricant to mold sliding parts and guiding components to prevent wear and corrosion.
- Inspection and Repair: Regularly inspect mold wear conditions and promptly repair or replace worn parts to extend mold service life.
Differences Between Thermoplastic and Thermoset Compression Molds
| Item | Thermoplastic Compression Molds | Thermoset Compression Molds |
|---|---|---|
| Material Characteristics | Softens when heated, hardens when cooled, can be reheated and reshaped | Irreversibly hardens after forming |
| Forming Cycle | Short heating and cooling cycle, high production efficiency | Longer curing time, relatively lower efficiency |
| Product Performance | Lower strength, suitable for general load-bearing products | Higher strength, superior heat and chemical resistance |
Conclusion
Thermoplastic compression molds have become essential production tools in various industries due to their efficient production capacity, excellent product performance, and wide application range. For businesses, selecting suitable mold materials, optimizing manufacturing processes, and maintaining the molds properly are key factors in improving product quality and production efficiency.
