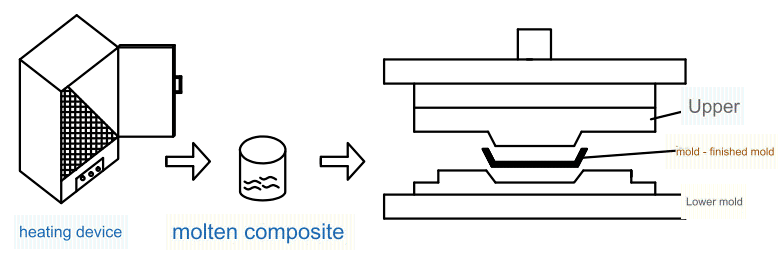
Compression molding, a process used for making products like SMC molds and compression molds, is one of the oldest and most dynamic methods for producing composite materials. This technique involves placing a specific amount of premixed or pre-impregnated material into a metal mold, such as composite molds or trunk board molds, which is then heated and pressed to form the final product. The process is highly efficient and offers numerous advantages for specialized and automated production.
Main Advantages of Compression Molding
- High production efficiency, ideal for specialized and automated manufacturing, particularly in applications such as SMC ceiling or SMC battery cover production.
- Precise product dimensions with excellent repeatability, used in the manufacture of engine splash shield molds and other automotive parts.
- Polished surfaces, eliminating the need for secondary finishing, which is useful for producing high-quality products like SMC water tanks or FRP tooling.
- Ability to mold complex structures in a single process, such as EV battery enclosures or sheet molding compound molds.
- Cost-effective for mass production due to lower material and labor costs, particularly in compression tooling or SMC bathroom products.
Although compression molding is highly beneficial, it does have some limitations. The molds, such as SMC tooling or BMC molds, are complex and require significant investment, and the process is best suited for mass production of small to medium-sized composite parts. However, with advancements in metal processing, press machine technology, and synthetic resin properties, the tonnage and size of presses have increased, allowing for the production of larger parts like SMC water tanks and GMT molds. Today, compression molding can be used for large automotive components, such as engine splash shield molds or integrated bathroom units.
Types of Compression Molding Processes
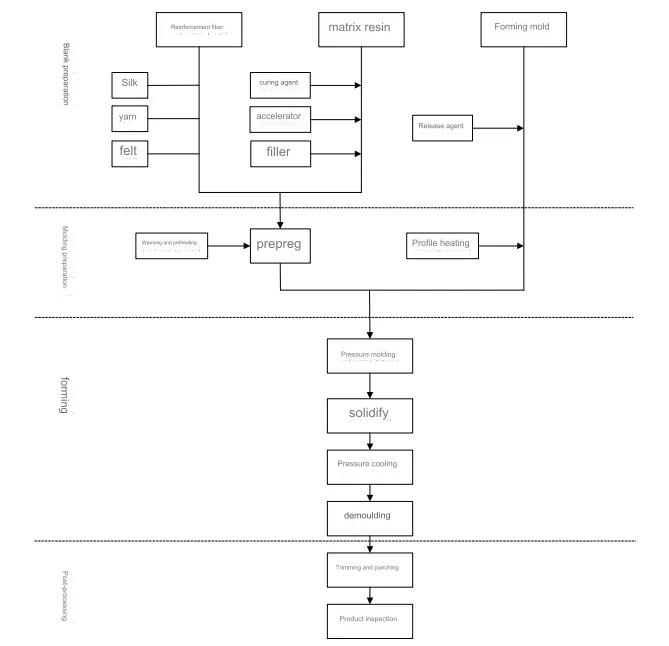
Compression molding processes can be categorized based on the type of reinforcement material and molding compounds used, such as LFT moulds or BMC tooling:
1. Fiber-Reinforced Molding
This process involves placing pre-mixed or pre-impregnated fiber materials into a metal mold. Under specific temperatures and pressures, composite material parts, such as composite molds or trunk board molds, are formed. This method is versatile and widely used, including in the production of products like SMC ceilings.
2. Scrap Fabric Molding
Scrap fabric molding involves cutting glass fiber cloth or other fabrics (such as jute, organic fiber, asbestos, or cotton cloth) into small pieces after being soaked in resin. These are then molded into composite parts, like those used in FRP tooling or compression molds, under heat and pressure in metal molds.
3. Fabric Molding
Pre-woven two- or three-dimensional fabrics are impregnated with resin, placed in metal molds, and subjected to heat and pressure to form composite parts. This process is particularly useful in producing complex parts like EV battery enclosures.
4. Lamination Molding
Layers of resin-impregnated glass fiber or other fabrics are cut into the desired shape and then molded in metal molds under heat and pressure. This method is commonly used for products like sheet molding compound molds or SMC bathroom components.
5. Filament Winding Molding
Continuous fibers or cloth (tapes) soaked in resin are wound under specific tension and temperature using a winding machine. These are then placed into molds for heating and pressing to form composite parts. This process is commonly used in compression tooling or FRP tooling.
6. Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) Molding
SMC sheets are cut based on the product's size, shape, and thickness, then layered and placed into a metal mold for heating and pressing. This method is frequently used in the production of products like SMC water tanks and SMC ceilings.
7. Preform Molding
Short fiber preforms are placed into a mold, and then a resin mixture (binder) is injected under specific heat and pressure to form the final product. This process is used in manufacturing various composite parts, including SMC molds and BMC tooling.

There are various types of molding compounds available, including pre-impregnated materials, premixed materials, and preforms. Popular compression molding materials include pre-impregnated cloth, fiber-reinforced premixes, and compounds like BMC, SMC, DMC, and TMC, used in processes for products like GMT molds or trunk board molds.
