Hot Press Mold and Hot Press Forming Mold: Process, Applications, and Advantages Analysis
- Suase /
- SUASE NEWS
Hot Press Molds and Hot Press Forming Molds are widely used in the composite materials industry, especially for SMC molds, BMC molds, LFT molds. This article provides a detailed analysis of their molding processes, characteristics, application fields, and future trends.
1. What is a Hot Press Mold?
A hot press mold is a type of mold that forms materials under high temperature and high pressure. It is commonly used for compression molding of composite materials such as SMC, BMC, and LFT, making it suitable for the automotive, aerospace, and electrical industries.
2. Process Flow of Hot Press Forming Mold
- Material Preparation: Cutting composite materials to the appropriate size.
- Heating: Preheating the material using heating equipment to the proper temperature.
- Mold Closing and Pressurization: Applying high temperature and pressure to fill the mold cavity.
- Curing and Cooling: Maintaining pressure until the material solidifies and then cooling.
- Demolding and Finishing: Removing the finished product and performing post-processing.
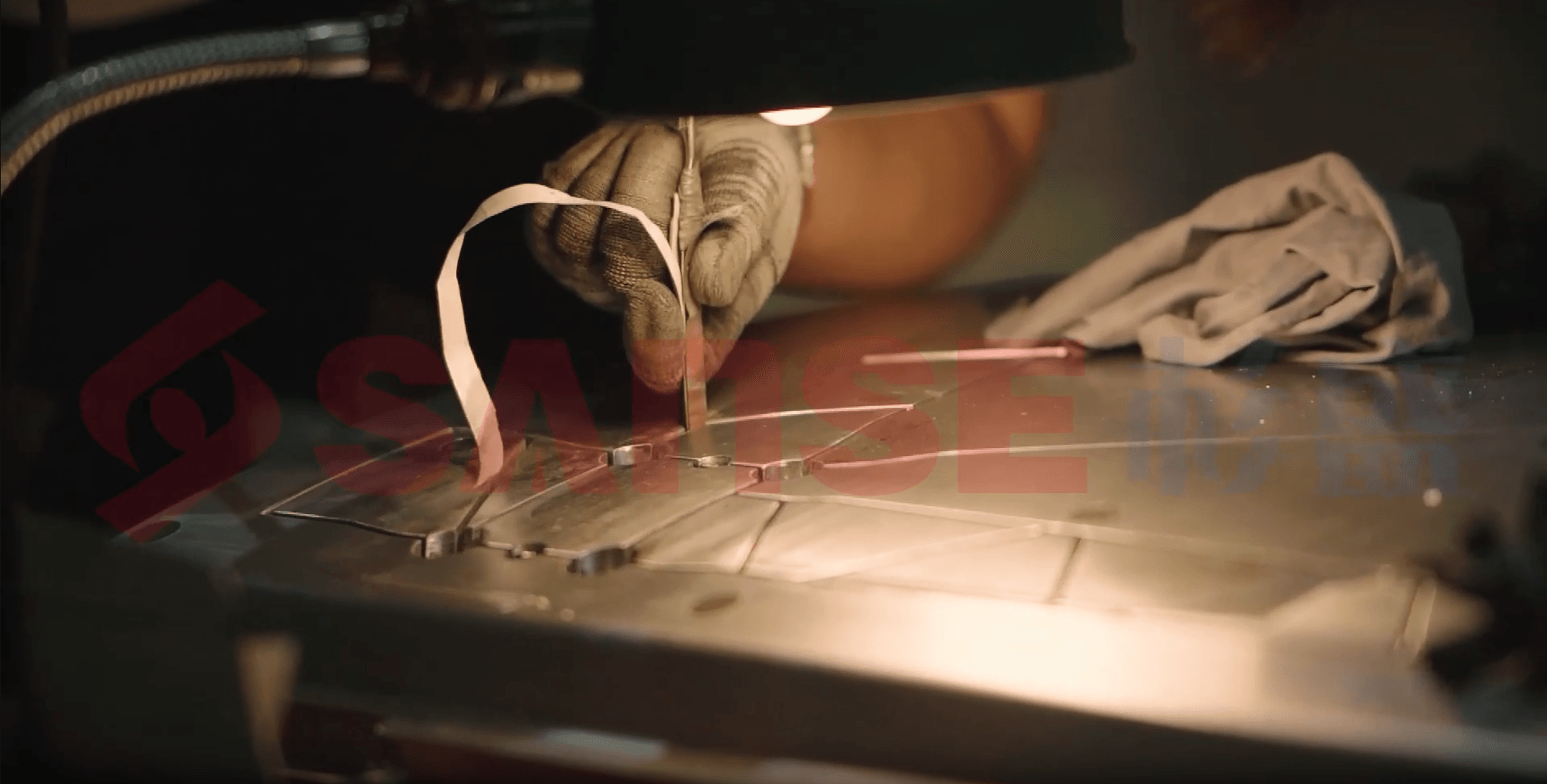
3. Characteristics of Hot Press Forming Mold
- High Precision: Ensures consistency in product dimensions.
- Compatible with High-Performance Materials: Suitable for carbon fiber, glass fiber, and other reinforced composites.
- High Forming Efficiency: Significantly improves production speed compared to hand lay-up processes.
- Stable Product Quality: Excellent mechanical properties and strong corrosion resistance.
4. Main Application Areas
4.1 Automotive Industry
Suitable for door panels, battery enclosures, bumpers, and other lightweight structural components.
4.2 Aerospace
Used for carbon fiber fuselage skins, wing components, engine covers, and other high-performance parts.
4.3 Electrical and Electronics
Applied in 5G antenna covers, cable protection housings, providing excellent insulation properties.
4.4 Construction and Infrastructure
Used for GRP/SMC water tanks, architectural decorative panels, and other high-strength lightweight materials.
5. Manufacturing and Optimization of Hot Press Molds
5.1 Selecting Suitable Mold Materials
Recommended materials include H13, P20, carbide, and other high-strength, wear-resistant alloys.
5.2 Structural Optimization
Optimizing flow channel design for uniform material filling; implementing heating and cooling systems for increased production efficiency.
5.3 Surface Treatment
Enhancing mold durability and demolding performance through chrome plating, nitriding treatment.
6. Future Trends of Hot Press Molds
- Intelligent Upgrades: Integrating sensors and AI optimization to improve precision.
- Eco-Friendly and Energy-Saving: Implementing low-energy heating systems to reduce carbon emissions.
- New Material Development: Advancing the application of higher-performance carbon fiber and glass fiber composites.
7. Conclusion
Hot press molds and hot press forming molds play a vital role in modern manufacturing, especially in the lightweight development of the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries. With the advancement of intelligent and energy-saving technologies, this process will become more efficient, promoting composite material applications to a higher level.
